Road infrastructure asset management is currently facing rapid digital transformation opening up new opportunities for the application of data from both traditional and new data sources, the ability to integrate data across multiple assets and the potential to improve efficiency in decision making throughout the asset lifecycle. However, there are challenges structuring, integrating, and linking data between different assets and data sources – especially those data contained separately within asset management and BIM platforms.
Data is vitally important to asset managers and supports decisions throughout the asset lifecycle. Although there has been progress integrating BIM into the operational phase of Assets, CoDEC is one of the first projects to consider this from the Asset Management side; creating practical methods to enrich data, data systems, and change our way of working.
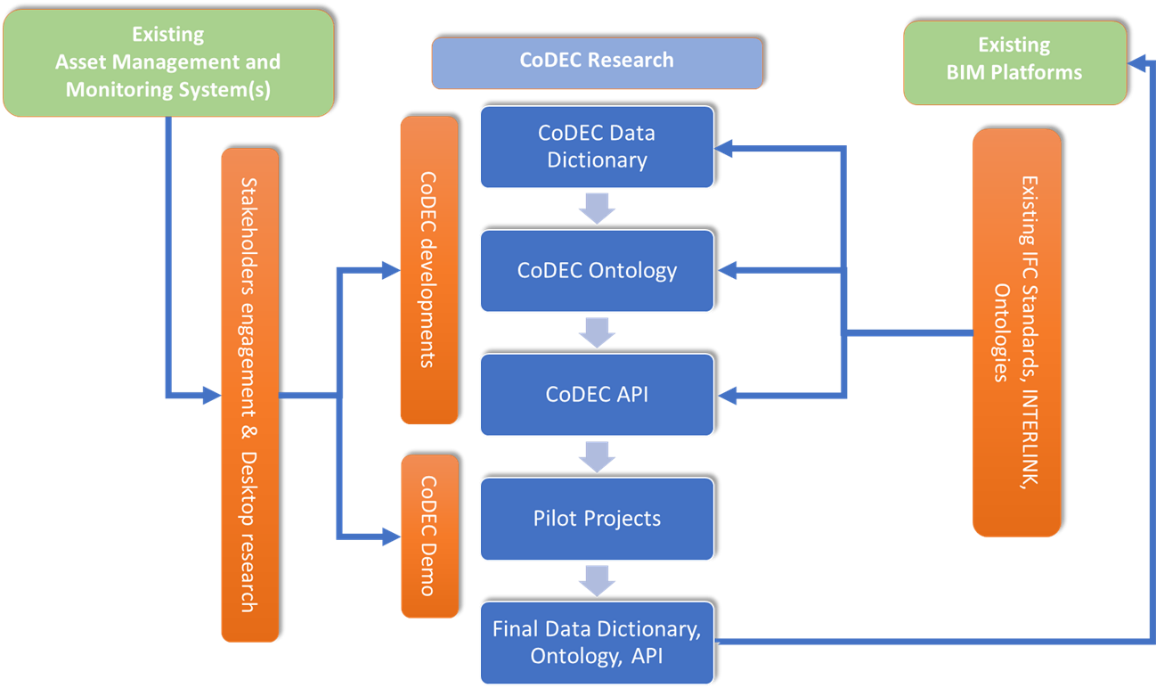
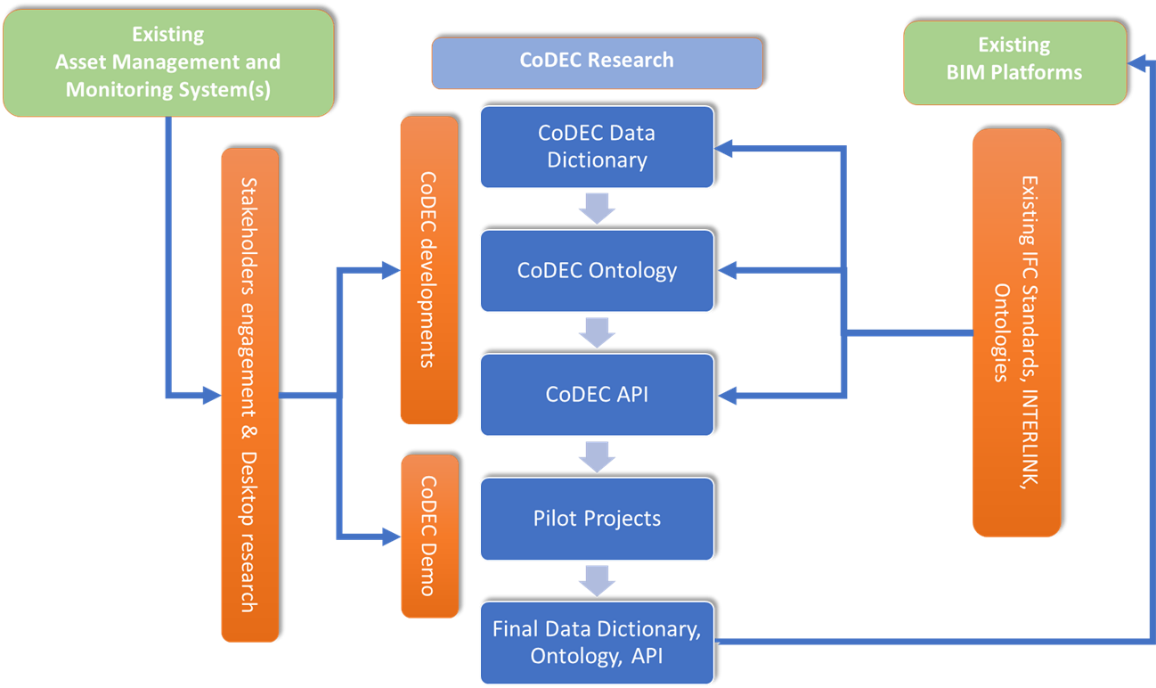
Building on the previous research projects, such as AM4INFRA and INTERLINK, CoDEC has applied a methodical approach to develop a framework for data (the data dictionary) and translate this into a machine-readable framework (the ontology) to make AMS and BIM data interoperable. This provides a step on the journey to making data seamlessly available when and where it is needed across data management systems, and supports the first steps in the transition from traditional Asset Management to operation via the Digital Twin.
CoDEC has aimed to provide practical and implementable outcomes that are also future-proof, by creating a framework that includes data provided by new technologies. The CoDEC project aimed to address these challenges by creating a Data Dictionary to link/integrate static and dynamic data for “key” infrastructure assets (including road pavements, bridges and tunnels). Having proposed such a dictionary, the potential benefits offered for connecting and linking data have been shown in three pilot projects to demonstrate
- how tunnel monitoring data can enrich BIM models of tunnels
- how data from bridge sensors can be linked and visualised
- how highway data generated at construction in a BIM model can be linked to asset-management GIS for the operational phase.
The results from these pilots present the challenges, lessons learned and practical benefits of linked data and semantic web technology to connect BIM to AMS and GIS platforms.
Although, Codec has not covered all road infrastructure assets and data types, it gives a structured and practical framework that can be easily expanded to include other asset types and data as required in the future - hence catering for Road Authorities’ future needs. The CoDEC methods and applications, are available for download from the CoDEC website.
A detailed description of the CoDEC Data Dictionary and CoDEC Data Ontology have been presented in Connected Data for Road Infrastructure Asset Management (Sukalpa et al) and Figure 1 provides an overview of the CoDEC processes and its outcome.
The pilot projects are being conducted with the support of three implementation partners: Agentschap Wegen & Verkeer (AWV, Belgian (Flemish) NRA) (Project 1); Rijkswaterstaat (RWS, Dutch NRA) (Project 2) and FTIA (Finnish NRA) (Project 3):
- Pilot project 1 – Tunnel - to show how the BIM model of a Tunnel can be enriched. It will link the BIM OTL to tunnel sensor data (such as thermal, visual sensors etc.) and provide an advanced 3D visualisation of this linked model.
- Pilot project 2 – Bridge - to integrate data from multiple bridge specific sensors, and demonstrate software tools and guidelines for linking, preparing and visualizing bridge data.
- Pilot project 3 – Highway – to link data between BIM models and a road network within a GIS (Geographic Information System) environment, requiring accurate spatial mapping between the two.
Although CODEC has successfully developed applications to integrate data from different systems, there is substantial work still to be done in this area. A key recommendation of this research is to encourage collaboration between asset owners (such as NRAs), standardisation bodies (such as ISO and IFC) and the software technology industry to understand the practical needs of asset managers/owners when it comes to data integration, and to build on the outcomes of this project to deliver the tools that will meet these needs.